4.1 Introduction
Most computer systems are now connected together in some way to form network.
This ranges from the basic school/home network of only a few computers to large networks such as internet which allows basically all computers connected to it to communicate with any other computer similarly connected.`
This ranges from the basic school/home network of only a few computers to large networks such as internet which allows basically all computers connected to it to communicate with any other computer similarly connected.`
4.2 Common types of network
Most networks are controlled by the use of servers.
-There are different types of servers:
-There are different types of servers:
- file servers: allow users to save and load data/files.
- applications servers: deal with the distribution of applications software to each computer.
- printer servers: ensure printing from devices on the network is done in a queue.
- proxy servers: used as a buffer between WANs and LANs.
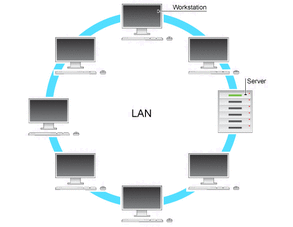
Local area networks (LANs) is a computer network that spans relatively small area.
-Advantages:
-Advantages:
- Sharing resources
- Communication between users
- a network administrator to control all aspects of the network
- Spread viruses throughout the whole network easily.
- Slower access to external networks, such as internet
- If the main server breaks down, in most cases the network will no longer function.
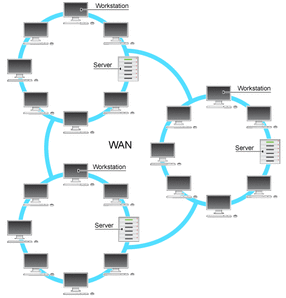
Wide area network (WANs) is a computer network that extends over a large geographical area.
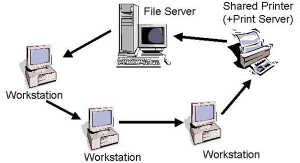
Ring networks
Every computer in the network is connected in a ring. Data is transmitted around the ring and each computer only removes the data which is relevant to it. Allows each computer to send and receive data since they all have a unique address.
-Advantages:
Every computer in the network is connected in a ring. Data is transmitted around the ring and each computer only removes the data which is relevant to it. Allows each computer to send and receive data since they all have a unique address.
-Advantages:
- Works well under heavy loading
- It is possible to create very large networks using this topology.
- If there is a fault in the wiring between two computers, the whole thing will fail.
- Adding a new device to the network can be difficult since it has to be placed between two existing devices
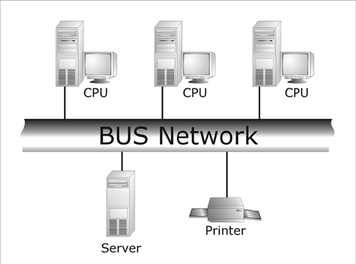
Bus networks
Each computer is connected to a common central line.
-Advantages:
Each computer is connected to a common central line.
-Advantages:
- Easy to add a new computer to the network
- If one device fails, it does not affect the rest of the network
- Does not need a hub or a switch and also requires less cabling than a star network
- Difficult to isolate any fault on the network
- If the central line has a problem, the whole system fails.
- This is becoming an increasingly outdated topology for network design.
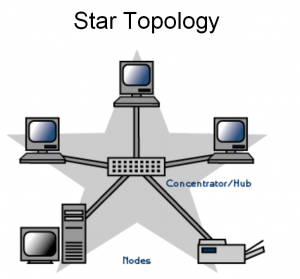
Star networks
Each computer is connected via a central hub or switch.
-Advantages:
Each computer is connected via a central hub or switch.
-Advantages:
- If one computer fails, nothing happen to other computers.
- Problems are easy to identify and work can be carried out on a faulty device without affecting the rest.
- Expand network easily.
- If the central hub breaks down, the whole network shut down.
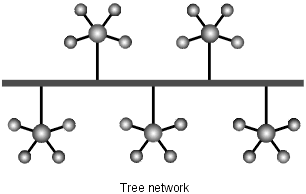
Tree network
Has a central line connecting to a series of star networks.
Has a central line connecting to a series of star networks.
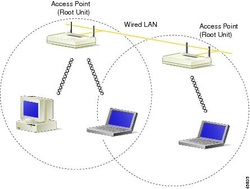
Wireless LANs (WLANs)
WLANs are nearly the same to LANs but there are no wires and cables. They provide wireless network communications over short distances using radio or infrared signals instead of cables.
Access points (APs): are connected into the wired network at fixed locations. The APs use either spread spectrum technology or infrared.
-Advantages:
WLANs are nearly the same to LANs but there are no wires and cables. They provide wireless network communications over short distances using radio or infrared signals instead of cables.
Access points (APs): are connected into the wired network at fixed locations. The APs use either spread spectrum technology or infrared.
-Advantages:
- All computers can access the same services
- There is no cabling.
- System is more flexible, since users can use their laptops.
- Adding new devices is very easy. (no costs of cabling)
- People can steal our password and connect to our internet, which makes it slower.
- There may be problems of interference which can affect the signal.
- The data transfer rate is slower than in a wired LAN.

WiFi
WiFi refers to any system where it is possible to connect to a network or to a single computer through wireless communications.
Examples:
WiFi refers to any system where it is possible to connect to a network or to a single computer through wireless communications.
Examples:
- on the WLAN described above
- PDAs and other handheld devices
- laptop computers which are WiFi enabled

Bluetooth is an example of wireless personal area networking (WPAN) technology
4.3 Network devices

Modem - is a device which converts a computer's digital signal into an analogue signal for transmission over an existing telephone line
- it is used to allow computers to connect to networks.
- it is used to allow computers to connect to networks.

Network hubs are hardware devices that can have a number of devices/computers connected to them

Switches are similar to hubs but they are more efficient in the way they distribute data.
-Each device has a media access control (MAC) address which identifies uniquely.
-Each device has a media access control (MAC) address which identifies uniquely.
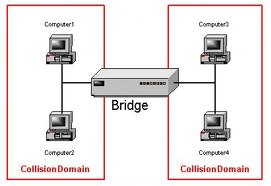
Bridges are devices that connect one LAN to another LAN that uses the same protocol.

Routers
- Routers are often used to connect the LANs together and also connect them to the internet.
- Routers inspect the data packages sent to it from any computer on any of the networks connected to it.
- Since every computer on the same network has the same first part of an internet protocol (IP) address.
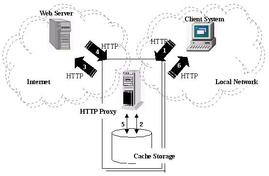
HTTP proxy servers
This is a special type of server that acts as a basic between a WAN and a LAN.
This is a special type of server that acts as a basic between a WAN and a LAN.
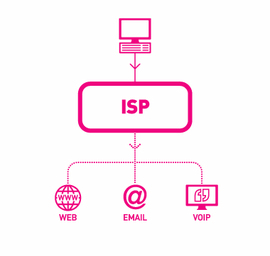
Accessing the internet
An ISP (Internet Service Providers) is a company that provides users with access to the internet
An ISP (Internet Service Providers) is a company that provides users with access to the internet

Dial-up internet access
This is the slowest internet ever (60kbps). A big disadvantage is that the telephone line is tied up while a dial up modem is in operation
This is the slowest internet ever (60kbps). A big disadvantage is that the telephone line is tied up while a dial up modem is in operation

Cable internet access
A form of broadband internet access that uses the cable television infrastructure.
A form of broadband internet access that uses the cable television infrastructure.
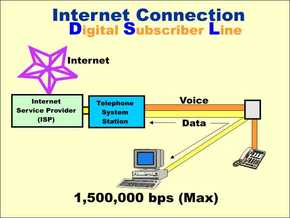
Digital subscriber line (DSL) (broadband) internet access
The fastest internet access (at least 11,000 kbps). A technology for bringing high- bandwidth information to homes and small businesses. The fast transfer rate allows systems such as voice over Internet Protocol (VOIP) and online chat rooms to be used effectively.
The fastest internet access (at least 11,000 kbps). A technology for bringing high- bandwidth information to homes and small businesses. The fast transfer rate allows systems such as voice over Internet Protocol (VOIP) and online chat rooms to be used effectively.
4.5 Intranets

(internal restricted access network) is as well as internet but it use for share information in small area or one building in company
- Advantages:
- Advantages:
- It is safe
- It can help business to prevent their employee from unwanted website
- Company can get specific information that they need
- Intranet has firewall . Do it with internet more difficult
- An intranet have limited information . Internet don't have
- An intranet can prevent certain internet site . Internet found it more difficult to do this
- An intranet is behind a firewall . That means it can give some protection against hackers